See other Immigration Articles
Title: 5 MILLION immigrants granted US citizenship can't speak English
Source:
[None]
URL Source: http://www.washingtonexaminer.com/5 ... -speak-english/article/2628443
Published: Jul 13, 2017
Author: AA
Post Date: 2017-07-13 09:54:48 by HAPPY2BME-4UM
Keywords: None
Views: 183
Comments: 1
In a stunning indictment of the system that tests immigrants on their eligibility to become "naturalized citizens," a new report finds that a third are functionally illiterate, unable to speak and understand enough English to get that status. Some 32 percent of naturalized citizens, about 5 million, fall below "basic" skills in English, the equivalent of being functionally illiterate, according to a new report from the Center for Immigration Studies. The report is a follow on to one that found 67 percent of immigrants in the United States for 15 years or more can't speak much English. According to the U.S. Customs and Immigration Services, those hopeful of becoming U.S. citizens must "be able to read, write, and speak basic English." They must also "have a basic understanding of U.S. history and government (civics)." While the immigrants apparently pass the minimum test, CIS looked also to a more authoritative test conducted by the Program for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies and found that in reality many immigrants are functionally illiterate. The tests, done before President Trump took office, suggest that 32 percent of all naturalized citizens speak English "not well or not at all." Of those, nearly half were Hispanics. The author, Jason Richwine, an independent public policy analyst, concluded: How did millions of immigrants become citizens without basic English literacy? The simple answer is that the government's English test is far less demanding than the PIAAC test. The PIAAC definition of literacy is "understanding, evaluating, using, and engaging with written text to participate in society, to achieve one's goals, and to develop one's knowledge and potential." Simply reading and writing basic English sentences does not necessarily meet that definition. As mentioned above, even some native English speakers struggle to apply their knowledge to language-intensive tasks. By contrast, naturalization applicants need only "read aloud one out of three sentences correctly" and "write one out of three sentences correctly" to prove their English ability. Does a person who passes this test sound ready to fully participate in the nation's social, economic, and civic interchange? Though its content already seems insufficient, the test is not even required of applicants who have reached certain age and residency milestones. If we are serious about new citizens developing functional English skills, the United States should adopt more rigorous language requirements.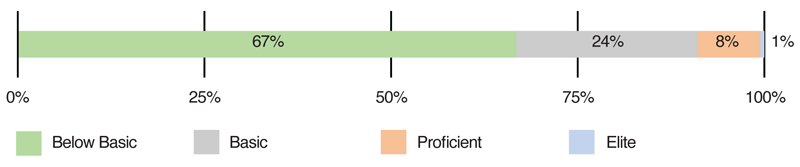
Post Comment Private Reply Ignore Thread
Top • Page Up • Full Thread • Page Down • Bottom/Latest
#1. To: All (#0)
by Josh Siegel | Jun 29, 2017 U.S. Constitution - Article IV, Section 4: NO BORDERS + NO LAWS = NO COUNTRY
Multiple states reject request from Trump's voter fraud commission to provide voter roll data
Officials in at least five states say they will reject a request by President Trump's voter fraud commission to turn over all publicly available voter roll data.
By late Thursday evening California, Kentucky, Virginia, Massachusetts and Connecticut signaled resistance to the request citing concerns over privacy, politics and one of the commission's top officials.
In a letter sent Wednesday to all 50 secretaries of state, the Presidential Advisory Commission on Election Integrity's vice chairman — Kansas Secretary of State Kris Kobach — requests the full names of all registered voters, their addresses, dates of birth, the last four digits of their Social Security numbers, voting history and other personal information.
The letter says that any documents submitted to the commission will also be made available to the public.
Alex Padilla, California's Democratic secretary of state, was the first to object to the request, releasing a statement Thursday vowing that he will "not provide sensitive voter information" to a commission that is pursuing "debunked claims of massive voter fraud."
"As secretary of state, it is my duty to ensure the integrity of our elections and to protect the voting rights and privacy of our state's voters," Padilla said. "I will not provide sensitive voter information to a commission that has already inaccurately passed judgement that millions of Californians voted illegally. California's participation would only to legitimize the false and already debunked claims of massive voter fraud made by the president, the vice president, and Mr. Kobach."
Padilla went on to call the commission a "waste of taxpayer money" and a "distraction from the real threats of the integrity of our elections today," which he considers to be Russia's interference in the 2016 campaign.
http://www.washingtonexaminer.com/multiple-states-reject-request-from-trumps-voter-fraud-commission-to-provide-voter-roll-data/article/2627525
Top • Page Up • Full Thread • Page Down • Bottom/Latest