Authored by Wolf Richter via WolfStreet.com, In the current craze that encompasses everything from sneakers and NFTs to stocks, where valuations don’t matter because of widespread certainty that valuations will be even greater in a few days, and where folks are chasing lottery-type returns, supported by the Fed’s interest rate repression and $3 trillion in asset purchases, and by the government’s trillions of dollars of handouts and bailouts – well, in this perfect world, there is a fly in the ointment: Vast amounts of leverage, including stock market leverage.
Margin debt – the amount that individuals and institutions borrow against their stock holdings as tracked by FINRA at its member brokerage firms – is just one indication of stock market leverage. But FINRA reports it monthly. Other types of stock market leverage are not reported at all, or are disclosed only piecemeal in SEC filings by brokers and banks that lend to their clients against their portfolios, such as Securities-Based Loans (SBLs). No one knows how much total stock market leverage there is. But margin debt shows the trend.
In February, margin debt jumped by another $15 billion to $813 billion, according to FINRA. Over the past four months, margin debt has soared by $154 billion, a historic surge to historic highs. Compared to February last year, margin debt has skyrocketed by $269 billion, or by nearly 50%, for another WTF sign that the zoo has gone nuts:
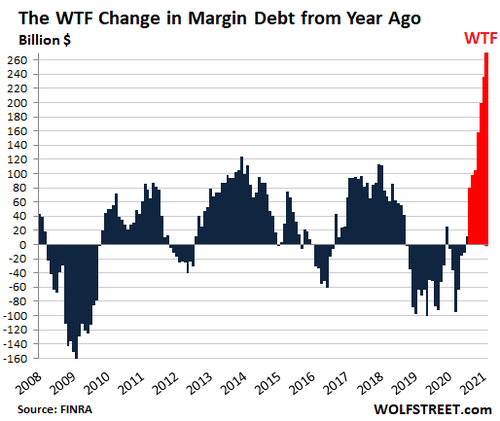
But margin debt is not cheap, especially smaller amounts. For example, Fidelity charges 8.325% on margin balances of less than $25,000 – in an environment where banks, money market accounts, and Treasury bills pay near 0%. Margin debt gets cheaper for larger balances, an encouragement to borrow more. For margin debt of $1 million or more, the interest rate at Fidelity drops to 4.0%
“Whether you need extra money for a short-term financing need or buying more securities, a margin loan may help you get the money you need,” Fidelity says on its website. In other words, take out a margin loan to buy a car or much needed bitcoin or NFTs.
Every broker has its own margin interest rate schedule. Morgan Stanley charges 7.75% for margin balances below $100,000, compared to Fidelity’s 6.875% for balances between $50,000 and $99,999. For margin balances over $50 million, Morgan Stanley charges 3.375%.
And it’s risky leverage for the borrower. It seems like risk-free leverage when stocks go up, but when your stocks do the unheard-of and tank below a certain level, your broker will ask you to put more cash into your account or sell stocks into the tanking market, whereby you then join the legions of forced sellers.
In the past, a big surge in margin balances tended to precede history-making stock market declines:
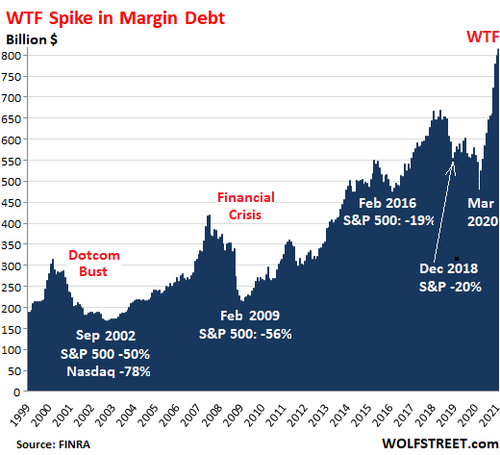
Over the two-decade period of the chart, the long-term changes in the dollar amounts are less important since the purchasing power of the dollar with regards to stocks has dropped.
But short-term, the changes show what is happening to margin debt in the run-up before the sell-off, and what is happening during the sell-off when margin requirements turn investors into legions of forced sellers.
Leverage is the great accelerator of stock prices, on the way up, and on the way down. Purchasing stocks with borrowed money creates buying pressure, and prices rise, and rising prices increase the margin balances a portfolio can support, and this encourages more stock-buying on margin.
On the other hand, selling stocks to deal with margin calls adds more selling pressure to an already declining market. The more prices fall, the more selling pressure there is from frazzled forced sellers trying to deal with margin requirements.
Then at some magic point, margin debt has been reduced enough, and its contribution to the selling pressure fades.
The historic surge in margin balances in recent months is another indicator of how hyper-speculative and blindly courageous the mega-bubble has become. All kinds of new theories are being proffered why fundamentals and valuations are meaningless, and why prices of all assets will shoot to the moon, no matter what.
These theories smacked into the bloodletting in Treasury bonds and high-grade corporate bonds with longer maturities, as long-term yields have been marching higher for months, which I discuss in my podcast…. THE WOLF STREET REPORT: Market Manias Galore, But Long-Term Interest Rates Smell a Rat
* * *