See other World News Articles
Title: Visualizing Earth's Tectonic Plates
Source:
[None]
URL Source: https://www.zerohedge.com/geopoliti ... alizing-earths-tectonic-plates
Published: Jul 11, 2022
Author: Tyler Durden
Post Date: 2022-07-11 23:31:23 by Horse
Keywords: None
Views: 40
It’s widely understood that Earth’s lithosphere (or outer crust) is made up of moving slabs of rock, better known as the tectonic plates. These plates only move a couple of inches each year. However, as Visual Capitalist's Carmen Ang explains below, these tiny movements add up over time and cause some of Earth’s most well-known phenomena. Today, the Earth looks a lot different than it did millions of years ago. This graphic by Giulia De Amicis provides a brief explanation of plate tectonic theory and shows a map of the seven major plates. Plate Tectonic Theory In the early 20th century, German geologist Alfred Wegener published a paper on his theory called continental drift—a hypothesis that Earth’s continents were moving across Earth, and sometimes, even colliding into one another. According to Wegener’s theory, Earth’s continents were once joined as a single, giant landmass, which he called Pangaea. But over time, Pangaea broke apart and formed the continents as we know them today. Wegener couldn’t explain why this phenomenon was happening, so at the time, his theory was heavily criticized by his colleagues. But over the years, technological advances allowed scientists to study the Earth more closely, and geologists started to build on Wegener’s theory. Discoveries like seafloor spreading helped explain the “why” behind continental movement, and eventually, Wegener’s initial continental drift theory morphed into plate tectonic theory. And now, the idea that Earth’s crust is slowly moving beneath our feet is widely accepted. The Seven Major Tectonic Plates There are seven major plates, and dozens of minor plates, that make up the outer crust of the Earth. The big seven are: North American plate Eurasian plate Pacific plate South American plate African plate Indo-Australian plate Antarctic plate The areas between these plates are known as plate boundaries, and their interactions cause some crazy things to happen on Earth’s surface. There are three types of plate boundaries: 1. Divergent boundary A divergent boundary is when two plates move away from each other, which creates a fracture in the lithosphere. A well-known divergent boundary is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which runs approximately 10,000 miles from the Arctic Ocean all the way down to the south of Africa. 2. Convergent boundary A convergent boundary is when two plates collide with one another. If the collision is between oceanic crust and continental crust, the lighter oceanic crust slides underneath the other plate, which is a process known as subduction. When two continental crusts collide, the rock folds and lifts at the boundary, creating mountains like the Himalayas (where the Indian plate meets the Eurasian plate). 3. Transform Boundary When two plates move parallel to one another, their meeting point is called a transform boundary. The friction causes tension. Eventually, that tension needs to be released, which can cause earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault is a well-known major transform boundary between the North American and Pacific plates—it caused the infamous San Francisco earthquake of 1906. Poster Comment: From Google: Is the New Madrid Fault a transform boundary (between 2 tectonic plates as California is between the Asian and North American plates)? While the fault zones on America's west coast (such as the San Andreas) are called “transform faults,” those in which the earth's tectonic plates rub against each other, the New Madrid zone is called an “intraplate zone,” meaning that it is a weak spot in the middle of the North American plate. I posted this because several of us live near the New Madrid fault zone. 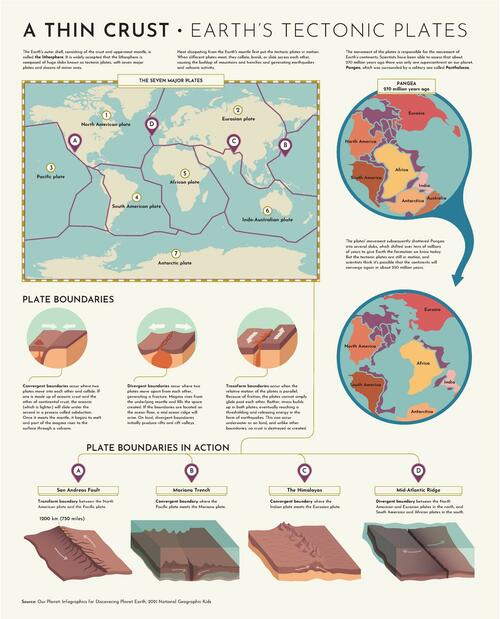
Post Comment Private Reply Ignore Thread